

Root canal system is a complex entity in itself. Success treatment of the root canal system depends upon the triad of thorough cleaning and shaping, disinfection & obturation up-to the calculated working length of the root canals. Failure to follow the Endodontology protocol can lead to failure of the endodontic treatment. Interpretation of a preoperative radiograph is an important step in laying out a correct treatment plan. Though, they are 2 dimensional but do give us an idea of what approximate type and number of root canals we will be dealing with in a particular case. Adhering to the steps of straight line access, glide path, biomechanical preparation with copious irrigation and 3-dimensional obturation seals the root canal system effectively.
This case report shows a Case of Irreversible pulpits with Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis (SAP) due to a deep Distal proximal lesion in a mandibular second molar(47).

Fig. 1
The tooth 47 was isolated after giving Inferior alveolar nerve block as well as buccal infiltration.
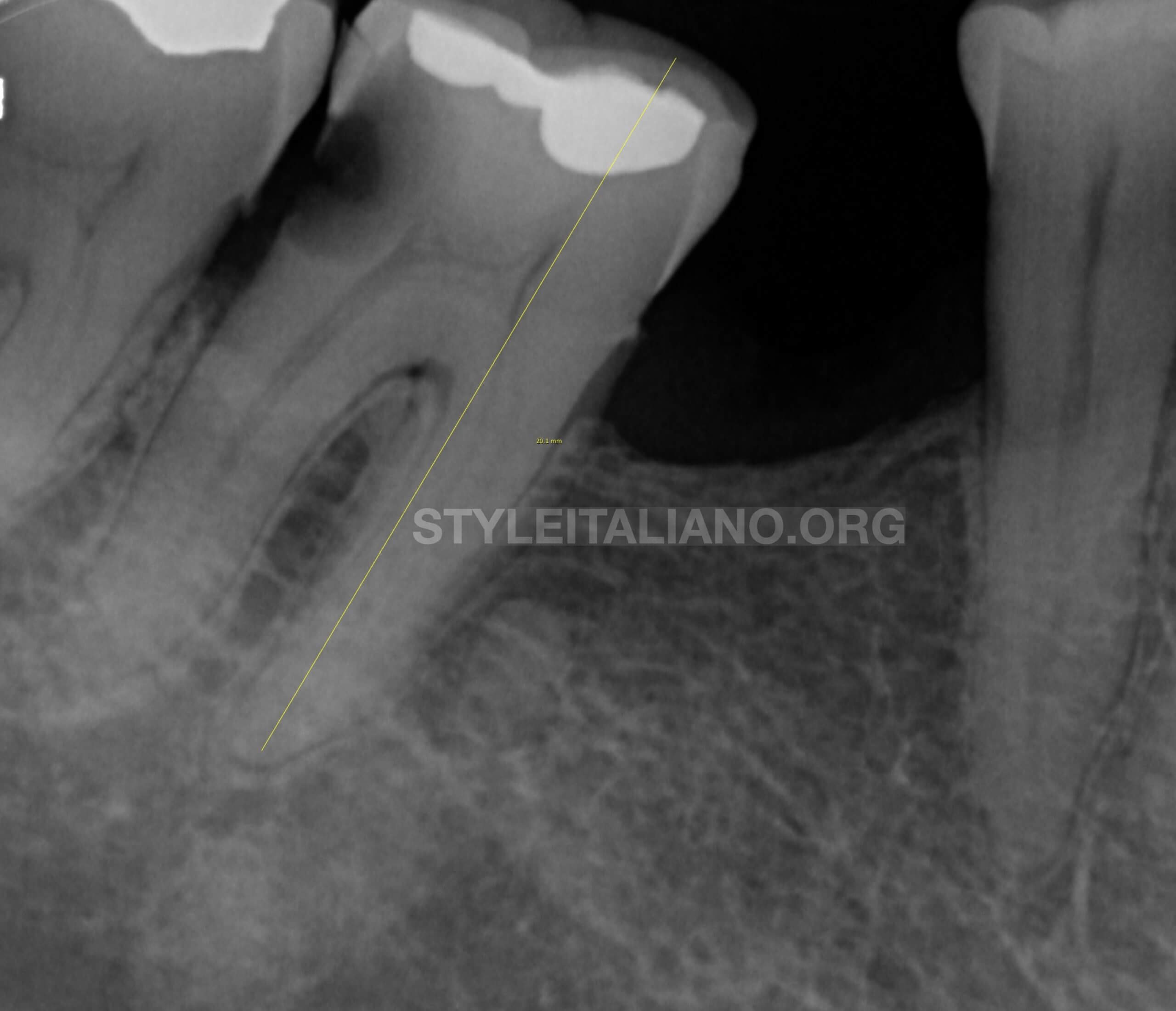
Fig. 2
Preoperative radiological assessment:
The periapical radiograph revealed deep distal carious lesion at 47.
The pulp chamber shows signs of calcifications. (Fig 1b).
Diagnosis (pulpal and periapical):
Irreversible Pulpitis with Symptomatic apical periodontitis.
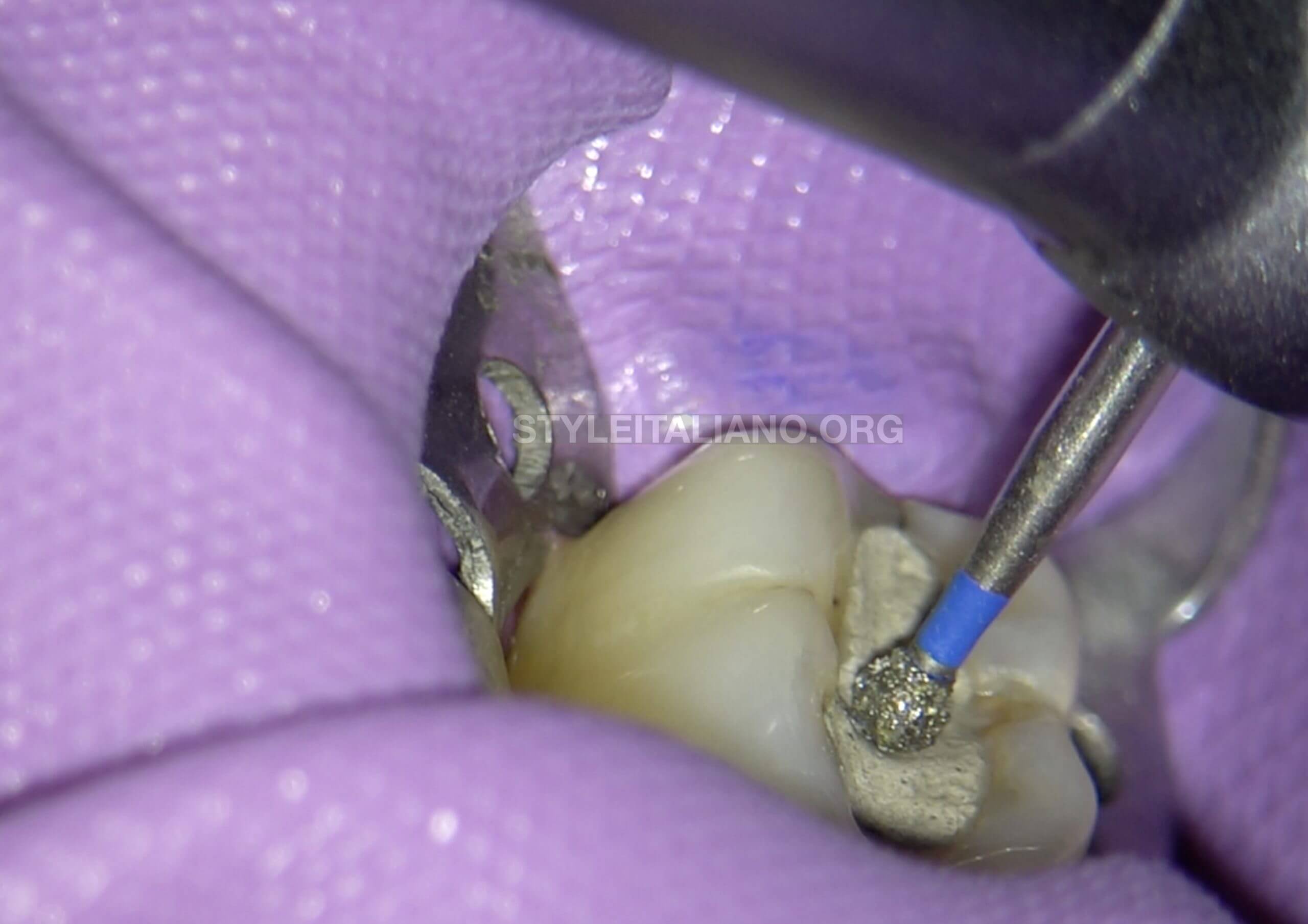
Fig. 3
Removal of the restoration was initiated in order to gain endodontic access. It was decided to break the distal wall and excavate the carious lesion and then attempt for endodontic access
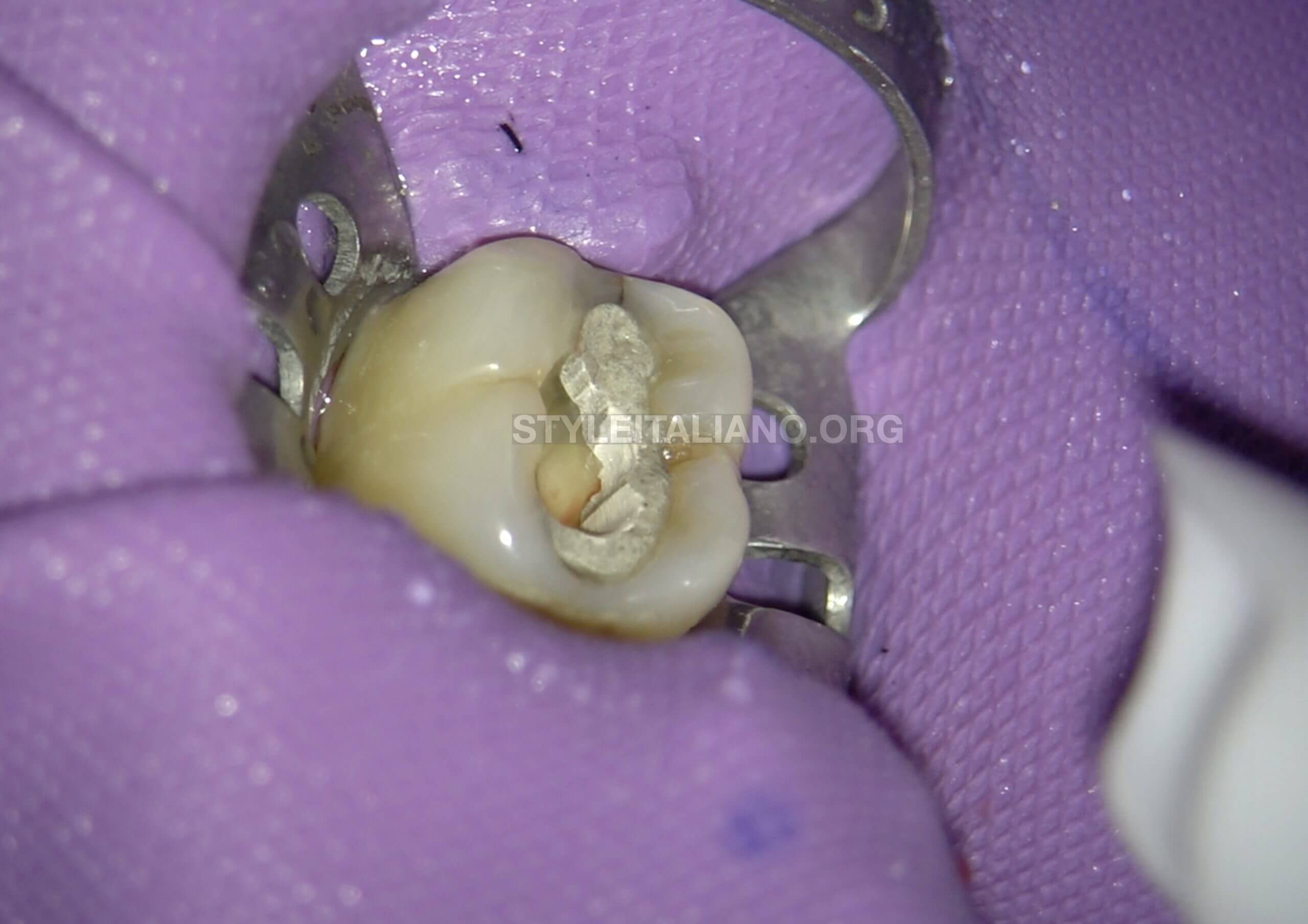
Fig. 4
During the excavation it was found that, although distal wall was carious, there was no visible break. Since the patient was in intense pain, it was decided to keep the wall intact and to go ahead immediately with Endodontic access in order to relieve the patient of pain, provide adequate wall throughout the treatment. The decayed wall will be broken later.
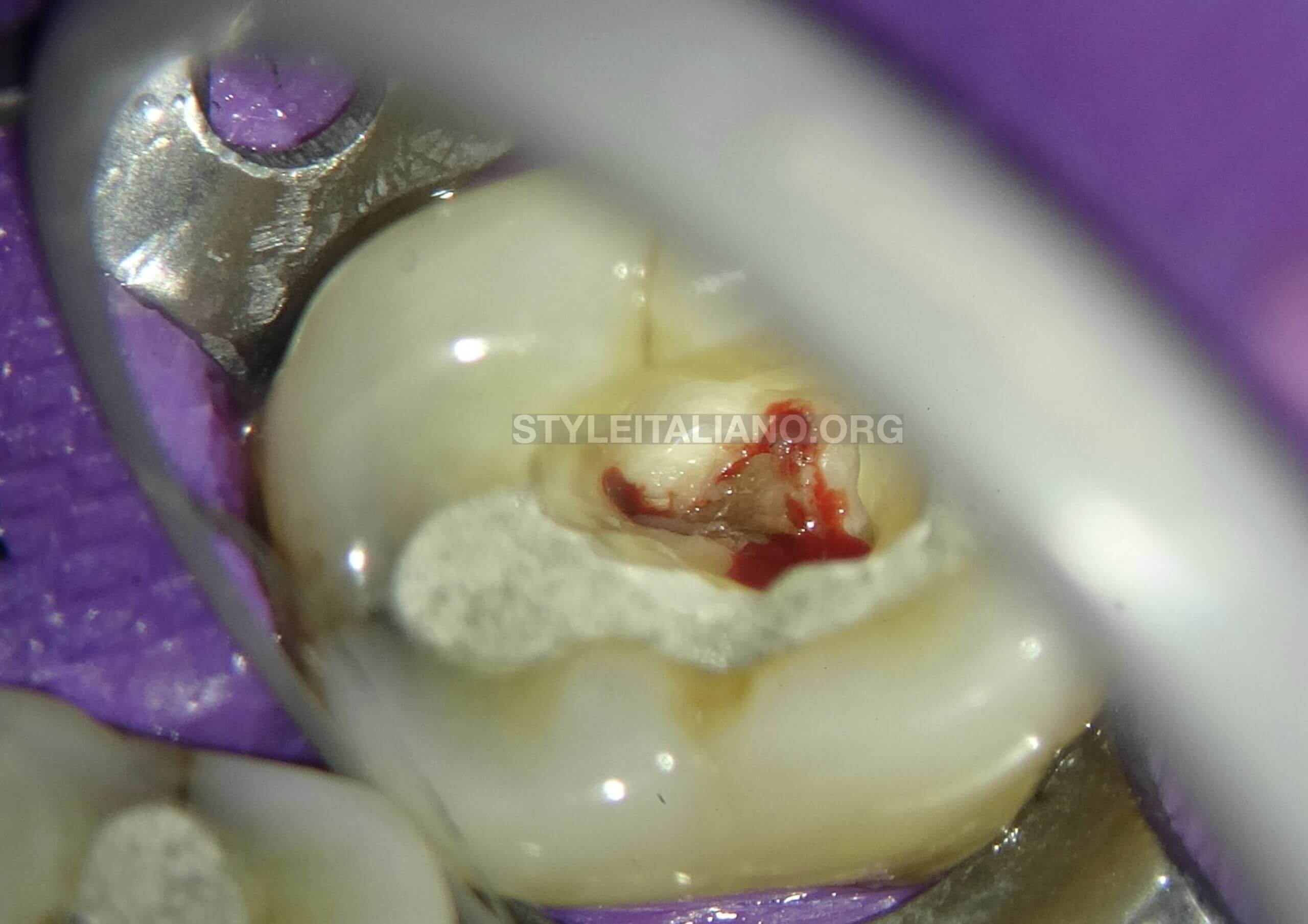
Fig. 5
Endodontic access was made and the bleeding was quite obvious from all the canals. The patient felt immediate relief once the access was made.
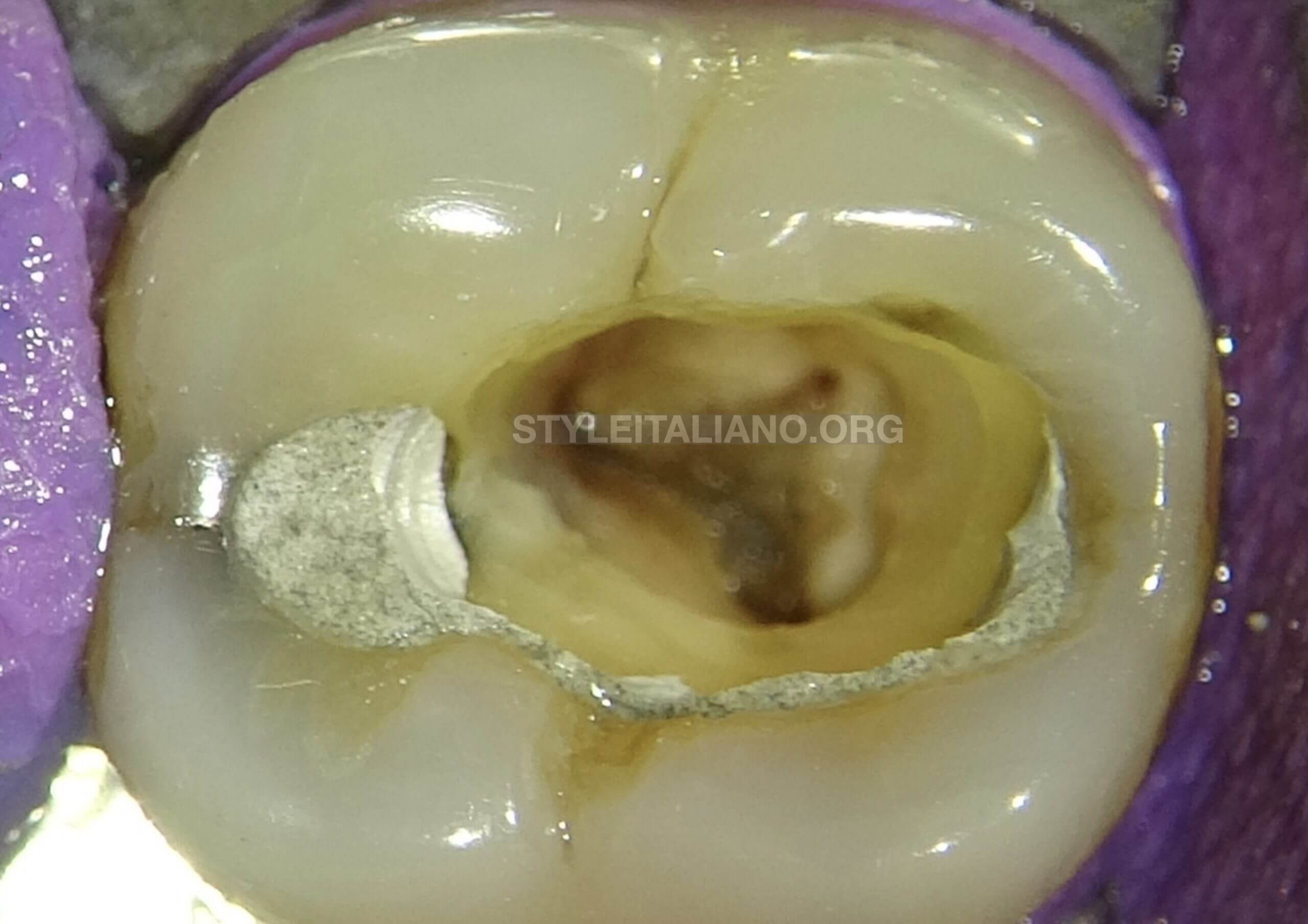
Fig. 6
The pulp was extirpated before initiating active cleaning and shaping
The coronal enlargement was done with starter opening file at 350rpm which reached till the middle of the canal. The file was used with EDTA as lubricant.
DO NOT use the files in dry canals and without Lubricant.
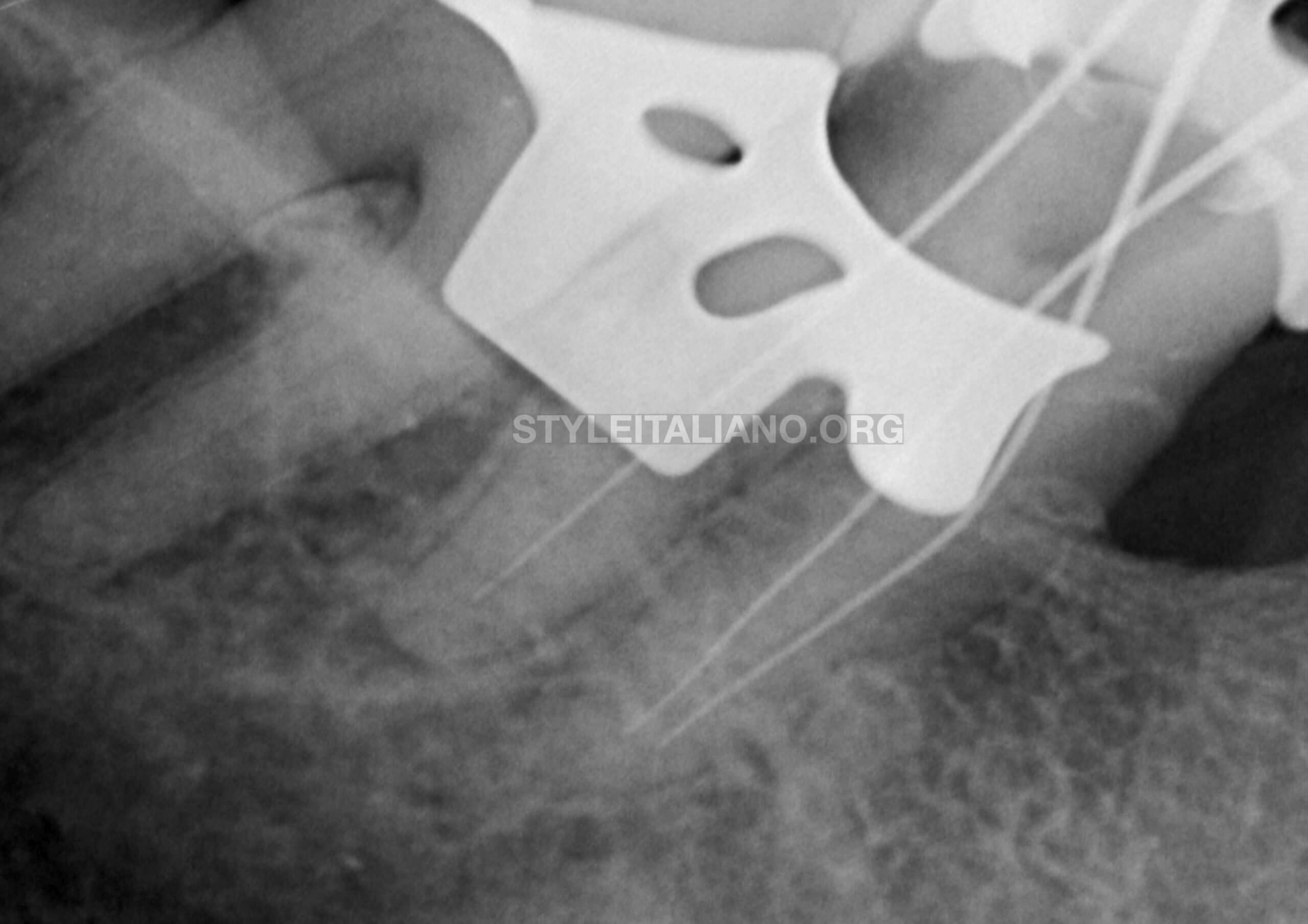
Fig. 7
The working length was taken with EAL and conformed on the radiograph.
The distal canal looked to be short and therefore it was readjusted.
The cleaning and shaping was performed with sequential instrumentation following the endodontic protocol. Copious irrigation was performed between the instruments.
Fig. 8
Master cone trial in was done and verified on the radiograph
Premixed BC sealer was used and applied inside the canals with the syringe delivery system. The master cones were coated with the sealer and placed inside the canals.
The gutta percha points were cut at the orifice with the heat gun
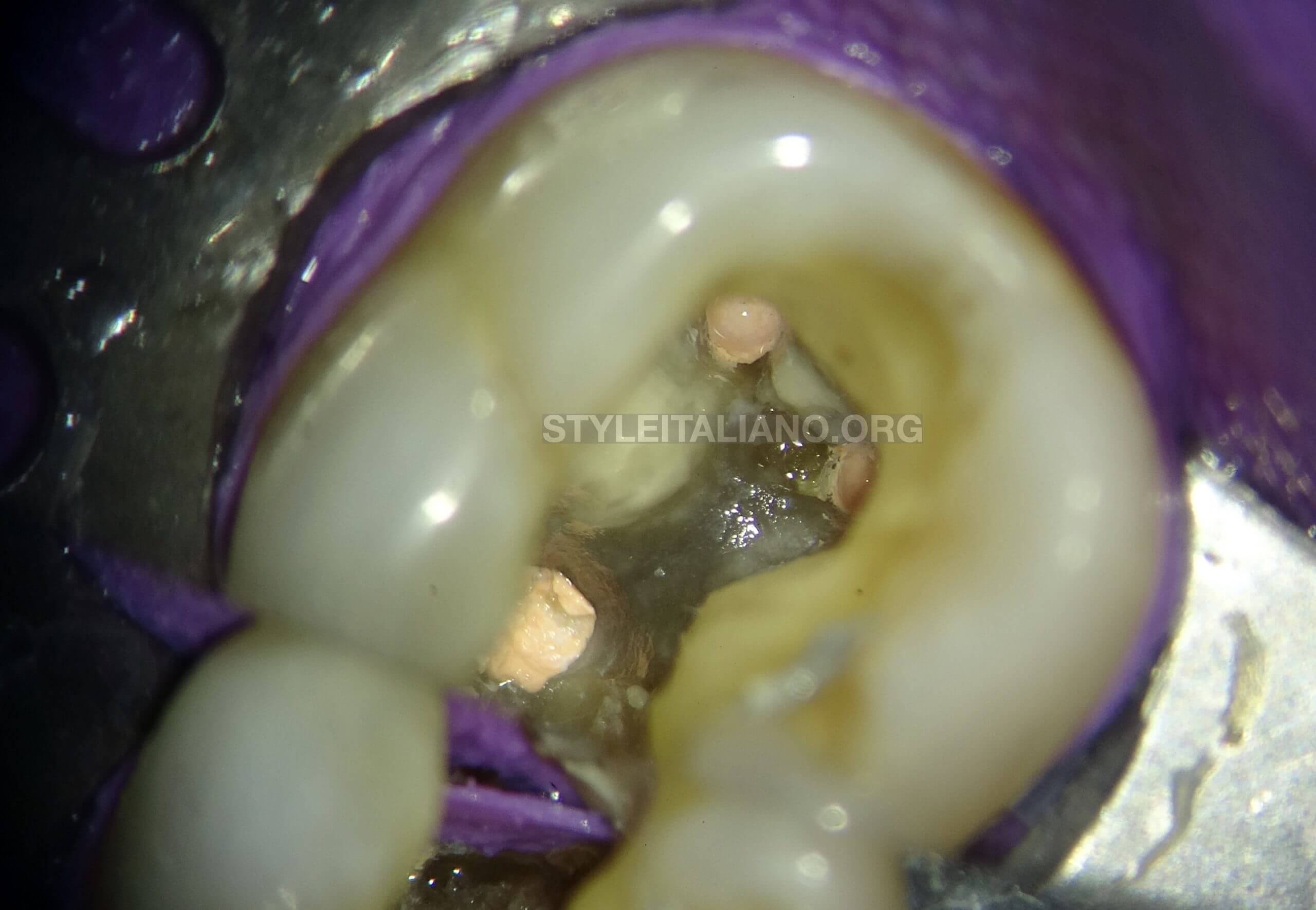
Fig. 9
The canals were obturated till the orifice and the pulp chamber cleaned of any gutta percha or sealer. The distal wall was cut and caries excavation done
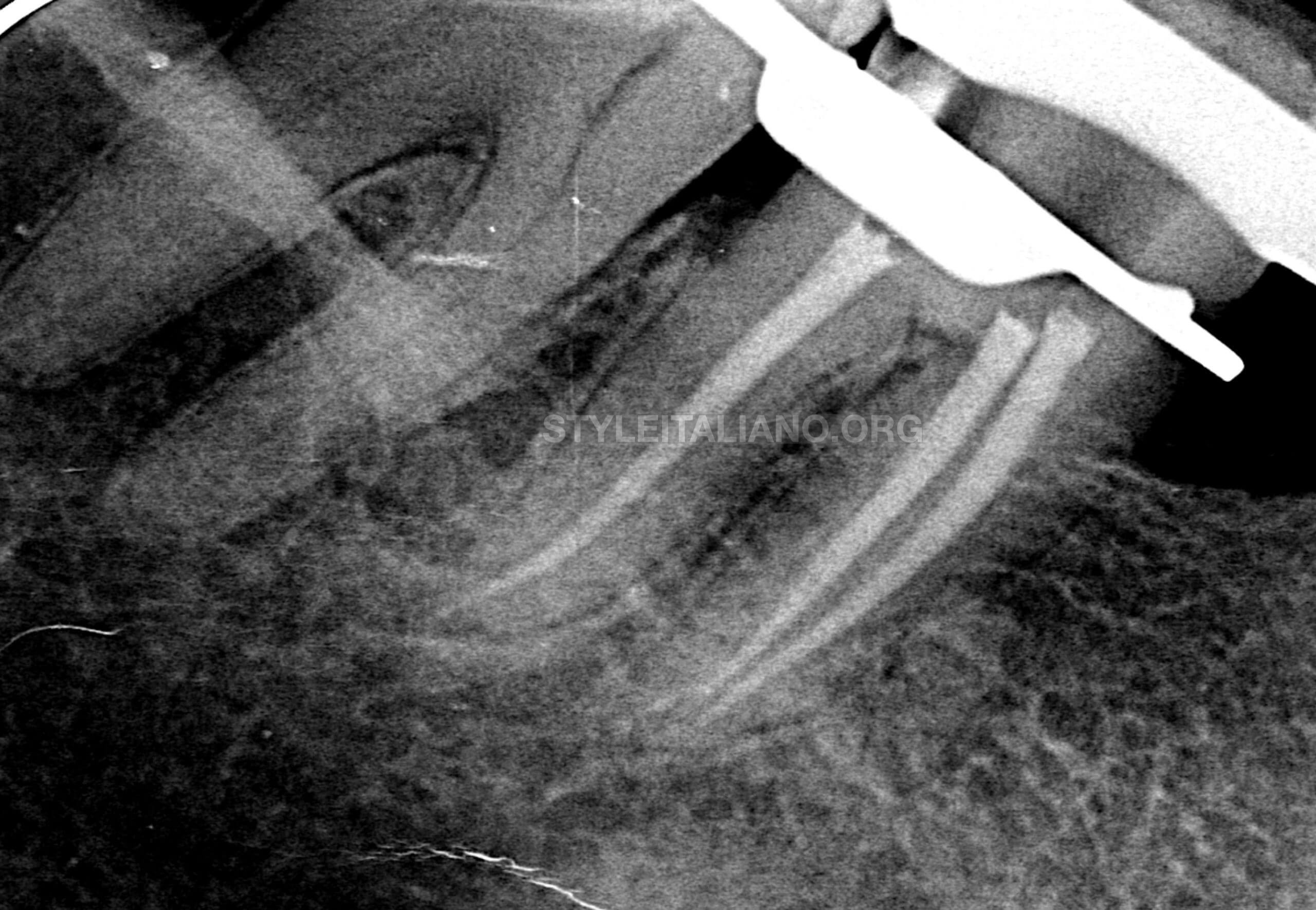
Fig. 10
Immediate postoperative radiograph was taken to verify the final obturation
Conclusions
In order to achieve success in endodontic treatment, root canal system needs to be thoroughly cleaned, shaped, disinfected and a 3-dimensional obturation of the root canal system should be achieved.
Selection of correct rotary file system is a very essential step to achieve successful cleaning and shaping of the root canal system.
The design of these instruments helps to achieve adequate cutting efficiency while respecting principles of Minimal Invasive Endodontics.
Bibliography
1. Mărgărit R, Andrei OC. Anatomical variations of mandibular first molar and their implications in endodontic treatment. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011 Jan 1;52(4):1389-92.
2. de Pablo ÓV, Estevez R, Sánchez MP, Heilborn C, Cohenca N. Root anatomy and canal configuration of the permanent mandibular first molar: a systematic review. Journal of endodontics. 2010 Dec 1;36(12):1919-31.
3. Smith CS, Setchell DJ, Harty FJ. Factors influencing the success of conventional root canal therapy—a five‐year retrospective study. International endodontic journal. 1993 Nov;26(6):321-33.
4. Stewart GG. The importance of chemomechanical preparation of the root canal. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology. 1955 Sep 1;8(9):993-7.
Whether you are a beginner or an expert, this event will give you the opportunity to learn and progress

Product consultant one-on-one service

Free product solutions

Professional team meticulous answer